In an era where environmental concerns are becoming increasingly prominent, sustainability has emerged as a driving force in the design and production of furniture and home accessories. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the environmental impact of their purchases, leading to a growing demand for sustainable furnishings.
We hear a lot about the horrors of fast fashion and how fast we consume our clothes. These end up in the land field or the ocean. But honestly, the furniture industry is not so far behind. Most furniture produced nowadays ( mostly still in the Far East) is only made to last a few years and a lot is made with MDF -Let us not forget that most MDF contains formaldehyde some can be specified as NAF (no-added-formaldehyde).
So understanding the whole lifecycle of the sustainable furnishing and finishings we put into our home is important, not just for our health, but for the impact on the environment.
One crucial tool in assessing and achieving sustainability in the world of interior design is the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). In this article, we will make a compelling case for furniture sustainability and demonstrate how Life Cycle Assessment plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the products we introduce into our living spaces are environmentally responsible.
Life Cycle Assessment is by now, a standard part of the process in buildings ( LEED) however it is certainly overlooked for what concerns interior design.
1. The Urgency of Sustainable Furnishings
Before delving into the significance of Life Cycle Assessment, it is essential to understand why sustainability in furniture and home accessories is critical. Here are some compelling reasons:
1. Resource Conservation: The production of furniture involves vast amounts of natural resources, such as wood, metal, and textiles. Unsustainable practices can lead to resource depletion and environmental degradation.
2. Energy Efficiency: Sustainable furnishings are often designed to be more energy-efficient during both their production and use phases. This can result in reduced energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Waste Reduction: The furniture industry generates a significant amount of waste, from manufacturing offcuts to discarded items. Sustainable design can minimize waste and promote recycling and repurposing. Also if produced well it will last longer
4. Health and Well-being: Sustainable materials and finishes can contribute to healthier indoor air quality, improving the overall well-being of occupants.
5. Biodiversity Conservation: Irresponsible logging and resource extraction can harm ecosystems and wildlife. Sustainable forestry and responsible sourcing practices help protect biodiversity.
2. Life Cycle Assessment: A Holistic Approach
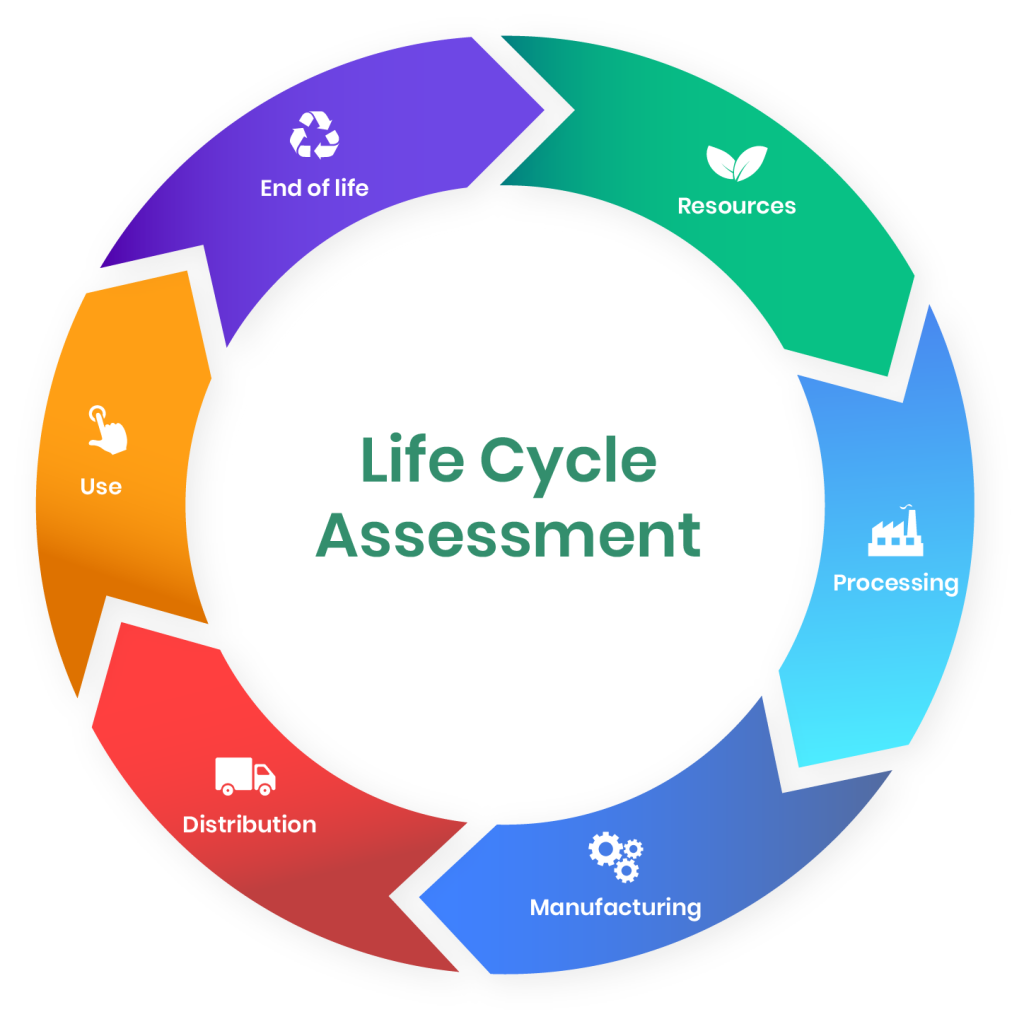
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a systematic approach used to evaluate the environmental impact of a product or service throughout its entire life cycle. It considers various stages, including raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, use, and end-of-life disposal. Let’s explore how LCA contributes to furniture sustainability:
1. Raw Material Selection: LCA helps manufacturers make informed choices regarding raw materials. For example, when producing wooden furniture, LCA can assess the environmental impact of different wood sources, promoting the use of sustainably harvested timber (FSC is the bare minimum). This can cover also other materials for example textiles, with the main certification being (GOTS – Global Organic Textile Standard), many other materials follow suit each with a certification that can follow the source of the materials
2. Manufacturing Processes: By analyzing energy consumption, emissions, and waste generation during manufacturing, LCA encourages more efficient production methods, reducing environmental burdens and the impact on the local community.
3. Transportation: LCA evaluates the transportation of materials and finished products, encouraging the selection of eco-friendly transportation options and optimizing logistics to minimize emissions. This includes options to source locally where equivalent options are available.
4. Product Use: LCA takes into account how furniture is used and its impact on energy consumption. Sustainable design principles can lead to longer product lifespans and lower energy requirements. A longer life span ought to induce lower turnover and let us not forget the number one rule of sustainability is to consume less.
5. End-of-Life Management: Furniture disposal can contribute to landfill waste (or ocean) and environmental harm. LCA promotes recycling, repurposing, or responsible disposal, reducing the overall ecological footprint. For more on recycling and repurposing head over to our post “Recycle, Upcycle, or simply consume less”
3. A Case Study: The Sustainable Sofa
To illustrate the importance of LCA in furniture sustainability, let’s consider a case study: the sustainable sofa.

1. Raw Material Selection: LCA informs the choice of materials for our sofa. For instance, opting for FSC-certified wood ensures sustainable forestry practices, reducing deforestation. But also let us consider the details of the fabric for example if this is a natural fabric with no extra chemical treatment for fire-retardant or anti-spill it can be recycled. Then how about the foam? If we are using natural latex this is biodegradable. So yes let’s break down the sofa and look at every single component
2. Manufacturing Processes: LCA assesses the environmental impact of different production methods. Energy-efficient manufacturing processes and water-saving techniques can significantly reduce carbon emissions. Although the production process does not impact the recyclability of the final product it does have an impact on the overall Impact of the product. so if we want to go into even further detail we would be looking at the sustainability and regenerative actions of the company as a whole.
3. Transportation: Reducing transportation means also reducing the carbon footprint, so choosing locally sourced materials IF they match the sustainability & quality criteria necessary for the product, would be a good solution.
4. Maintenance: Sustainable design principles, such as using durable materials and replaceable cushions, extend the sofa’s lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
5. End-of-Life Management: LCA considers how the sofa will be disposed of when it reaches the end of its., so when designing a sofa being able to disassemble the single components and materials is key to making it circular at the end of life.
Some companies, that I know that are really attentive to the materials they use are:
In conclusion.
The interior design industry is moving fast – we are all well aware of the importance of sustainability, well-being, and even regenerative design. we now have to take real steps towards making it effective and start influencing the manufacturing process of the furnishings and finishes we actually put into our homes, offices, hotels schools, and healthcare. It is only a bottom-up approach that will really allow us to move forward.
